Testosterone is often thought of as a “male hormone,” but it also plays an important role in women’s health. In recent years, there has been growing recognition of the benefits of testosterone therapy for certain women—particularly in the management of hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) during the perimenopausal and postmenopausal years.
At The Health Suite Leicester, our menopause specialists follow NICE guidance and use a safe, evidence-based approach to prescribing testosterone when clinically appropriate.
Why Testosterone Matters for Women
Although testosterone levels in women are far lower than in men, it contributes to:
- Sexual function and libido
- Mood and overall well-being
- Energy levels and motivation
- Bone and muscle health
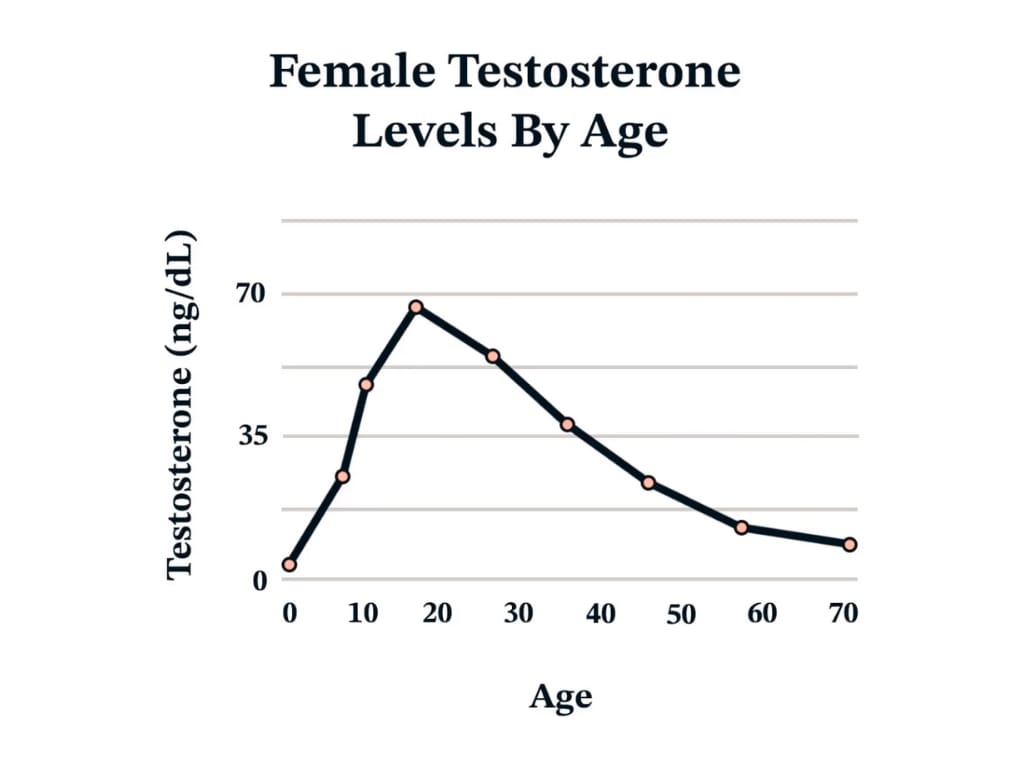
Levels naturally decline with age and fall sharply after the menopause, which may contribute to symptoms such as low sexual desire, reduced energy, and reduced quality of life (Islam et al., 2019).
What Do the Guidelines Say?
NICE NG23 (2015, updated 2024) recommends that clinicians consider testosterone supplementation in women with:
- Distressing low sexual desire after menopause, if HRT alone is not effective (NICE, 2024).
Clinical Knowledge Summaries (CKS) also state that testosterone can be prescribed “off-label” in women under specialist supervision for HSDD, provided patients are counselled about its use and monitored regularly (CKS, 2022).
The British Menopause Society (BMS) supports this, emphasising that testosterone may improve sexual desire and arousal in postmenopausal women, but is not recommended for use in women with other symptoms such as fatigue or mood alone (Panay et al., 2022).
Safety and Monitoring
Testosterone therapy for women is off-label in the UK, as there is currently no licensed preparation specifically for women. Instead, clinicians use carefully adjusted doses of products designed for men.
Safety points include:
- Baseline and follow-up blood tests (total testosterone, SHBG) to avoid over-replacement
- Prescribing by a menopause specialist trained in hormone therapy
- Monitoring for side effects such as acne, excess hair growth, or changes in mood
- Regular review of sexual function and overall wellbeing (NICE, 2024; Panay et al., 2022)
Evidence suggests that testosterone therapy is safe and effective when monitored appropriately, with no increase in cardiovascular or breast cancer risk seen in short- to medium-term studies (Islam et al., 2019)
When Testosterone May Help
Testosterone may be considered in:
- Postmenopausal women experiencing low libido not relieved by oestrogen/progestogen HRT
- Women who have undergone surgical menopause and report loss of sexual desire
- Selected perimenopausal women with distressing low sexual desire and confirmed low levels, under specialist care
It is not recommended for:
- Generalised fatigue, mood disturbance, or cognitive symptoms without sexual dysfunction
- Women with high baseline testosterone levels or contraindications
Why Choose The Health Suite for Testosterone Assessment
At The Health Suite Leicester, our BMS-accredited menopause specialist provides:
- Full menopause and hormone health assessment
- Care aligned with NICE, CKS, and BMS guidelines
- Safe prescribing with regular blood monitoring
- Individualised plans that integrate lifestyle, nutrition, and advanced testing if required
If you are experiencing low sexual desire or struggling with menopause symptoms, speak to our menopause specialist at The Health Suite Leicester. We provide safe, guideline-based hormone care tailored to your needs.
Book your consultation with our menopause specialist today
Hormone Support for Women: Testosterone Therapy at Our Menopause Clinic
References:
- Clinical Knowledge Summaries (2022) Menopause. Available at: https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/menopause/ (Accessed: 22 September 2025).
- Islam, R.M., Bell, R.J., Green, S., Page, M.J. and Davis, S.R. (2019) ‘Safety and efficacy of testosterone for women: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trial data’, The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, 7(10), pp. 754–766.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (2024) Menopause: diagnosis and management (NG23). Updated 5 March 2024. Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng23 (Accessed: 22 September 2025).
- Panay, N., Al-Azzawi, F., Bouloux, P., Davis, S.R., Fenton, A., Goldstein, I., Graziottin, A., Guay, A., Kingsberg, S., Laan, E., Shifren, J. and Simon, J. (2022) ‘Testosterone replacement in menopause: position statement of The British Menopause Society’, Post Reproductive Health, 28(2), pp. 69–87.
